Python Example Assemblies.py
About This Example:
A more involved and extensive example that uses the PDBX parsing Python library to generate a CIF file for each biological
assembly listed in the pdbx_struct_assembly
category of a CIF file. This example synthesizes information located in the
pdbx_struct_assembly_gen,
pdbx_struct_oper_list, and
atom_site categories to accomplish this task.
For every assembly in pdbx_struct_assembly_gen, the program retrieves the operation expression and applies the
operations it specifies (which are stored in pdbx_struct_oper_list) to certain coordinates.
Build Instructions:
Files: Assemblies.py, 2BUK.cif
Save Assemblies.py and the CIF data file. Run python Assemblies.py /path/to/file.cif, which generates a
/path/to/2BUK-ASSEMBLY.cif file for each assembly listed in pdbx_struct_assembly
Methods to Note
from pdbx.reader.PdbxContainers import ContainerBasefrom pdbx.reader.PdbxContainers import DataCategory
getObj(self, name)Returns the DataCategory object specified by name.getAttributeList(self)Returns a list of attribute/data item names.getRowCount(self)Returns the number of rows in the category table.getValue(self, attributeName=None, rowIndex=None)Returns the value of the attribute attributeName at row index rowIndex.getFullRow(self, index)Attempts to fetch the full row at index index and returns an empty list if it fails.setValue(self, value, attributeName=None, rowIndex=None)Sets a value for the attribute specified by attributeName at the row index rowIndex.
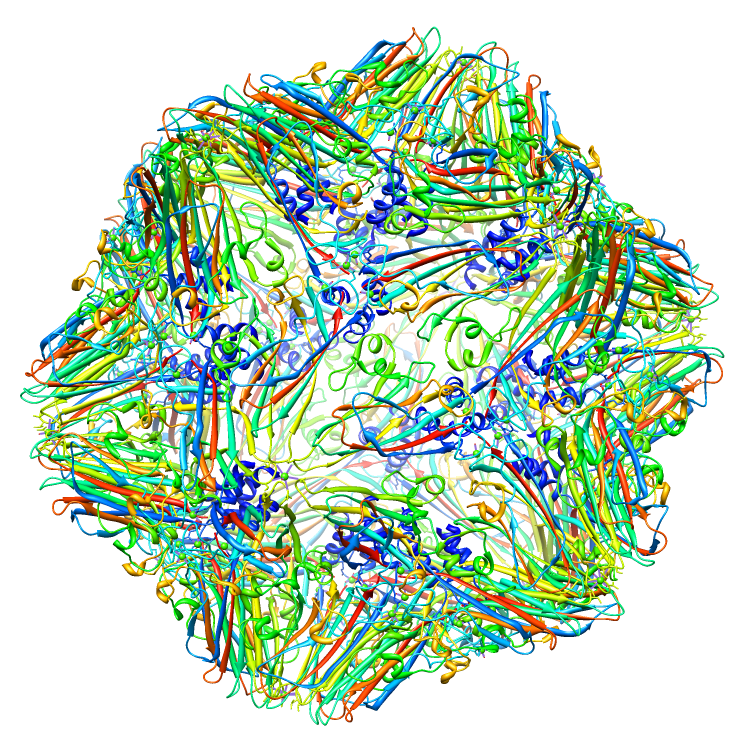
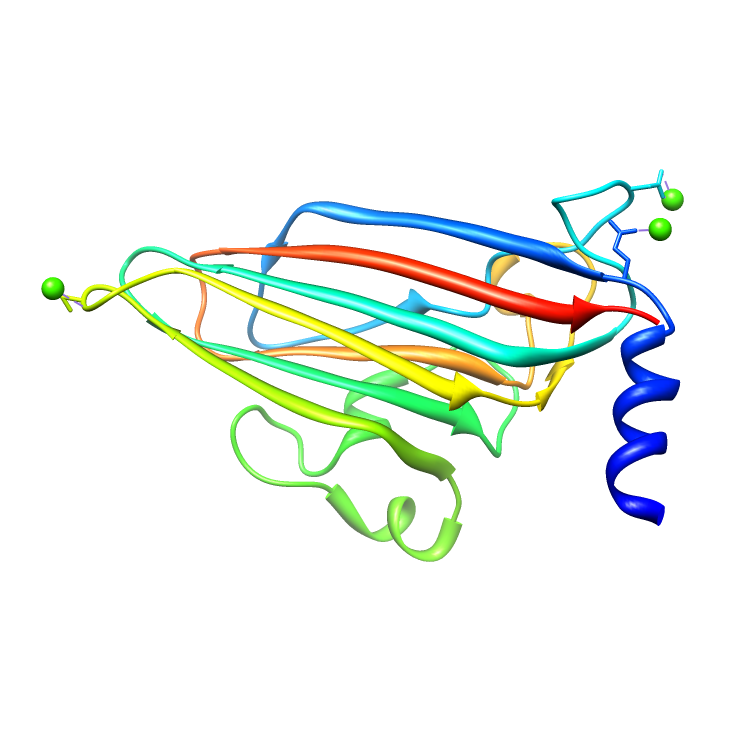
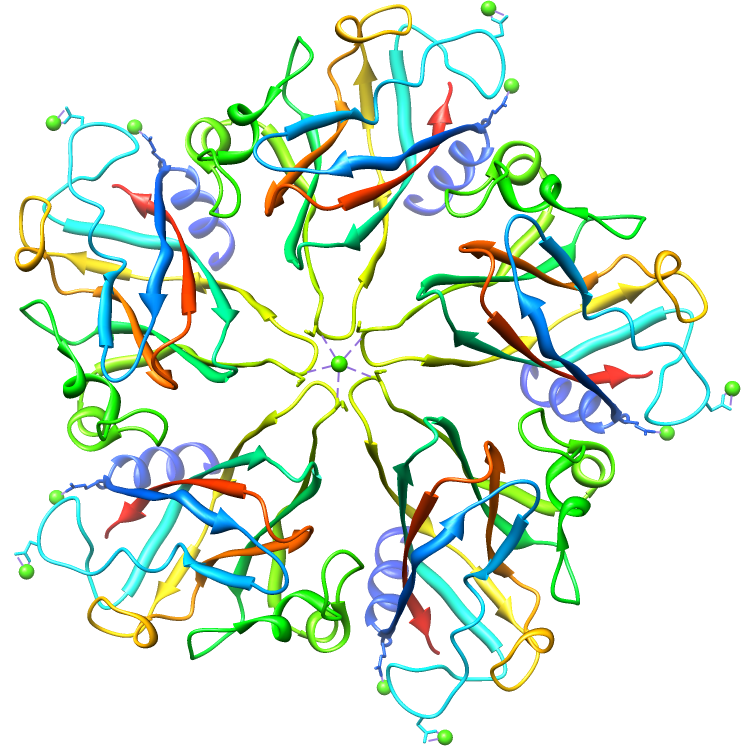
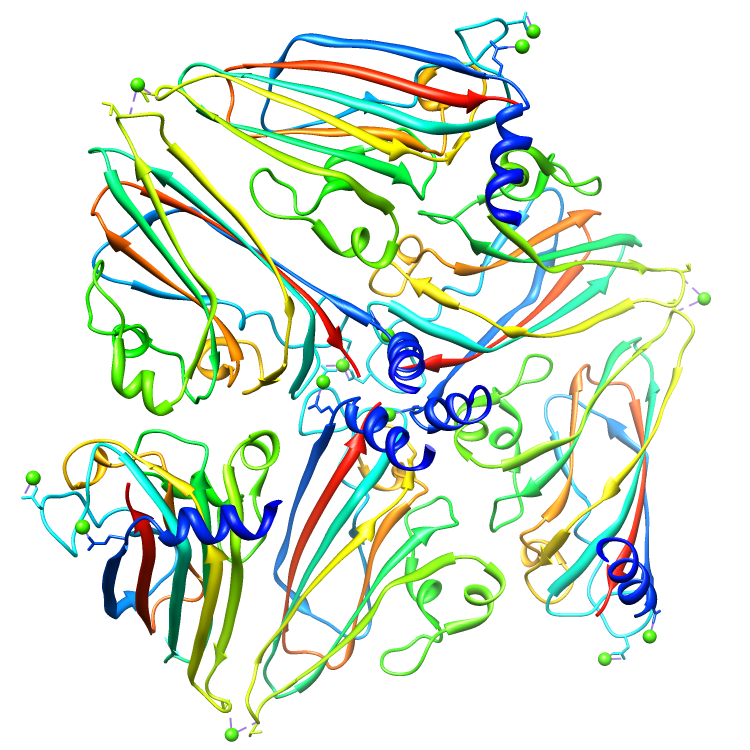
Assemblies for 2BUK.cif
Rendered via Chimera
Example Source Code
/*************************
* Assemblies.py
*
* For some CIF file, generate a complete CIF file for every assembly
* listed in the pdbx_struct_assembly category table by performing
* rotation and translation matrix operations and creating a new atom_site
* category table for each assembly.
*
* Lines with superscriptions contain footnoted references or explanations.
*************************/
import copy
from os.path import splitext
from pdbx.reader.PdbxReader import PdbxReader
from pdbx.writer.PdbxWriter import PdbxWriter
from pdbx.reader.PdbxContainers import *
from sys import argv
def parseOperationExpression(expression) :
operations = []
stops = [ "," , "-" , ")" ]
currentOp = ""
i = 1
# Iterate over the operation expression
while i in range(1, len(expression) - 1):
pos = i
# Read an operation
while expression[pos] not in stops and pos < len(expression) - 1 :
pos += 1
currentOp = expression[i : pos]
# Handle single operations
if expression[pos] != "-" :
operations.append(currentOp)
i = pos
# Handle ranges
if expression[pos] == "-" :
pos += 1
i = pos
# Read in the range's end value
while expression[pos] not in stops :
pos += 1
end = int(expression[i : pos])
# Add all the operations in [currentOp, end]
for val in range((int(currentOp)), end + 1) :
operations.append(str(val))
i = pos
i += 1
return operations
def prepareOperation(oper_list, op1index, op2index) :
# Prepare matrices for operations 1 & 2
op1 = [[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]]
op2 = [[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# Fill the operation matrices for operations 1 & 2
for i in range(3) :
op1[i][3] = float(oper_list.getValue("vector[" + str(i + 1) + "]", op1index))
if (op2index != -1) :
op2[i][3] = float(oper_list.getValue("vector[" + str(i + 1) + "]", op2index))
for j in range(3) :
op1[i][j] = float(oper_list.getValue("matrix[" + str(i + 1) + "][" + str(j + 1) + "]", op1index))
if (op2index != -1) :
op2[i][j] = float(oper_list.getValue("matrix[" + str(i + 1) + "][" + str(j + 1) + "]", op2index))
# Handles non-Cartesian product expressions
if (op2index == -1) :
return op1
operation = [[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1]]
# Handles Cartesian product expressions (4x4 matrix multiplication)
sum = 0.0
for row in range(4) :
for col in range(4) :
sum = 0.0
for r in range(4) :
sum += (op1[row][r] * op2[r][col])
operation[row][col] = sum
return operation
# Open the CIF file
cif = open(argv[1])
root, ext = splitext(argv[1])
# A list to be propagated with data blocks
data = []
# Create a PdbxReader object with the CIF file handle
pRd = PdbxReader(cif)
# Read the CIF file, propagating the data list
pRd.read(data)
# Close the CIF file, as it is no longer needed
cif.close()
# Retrieve the first data block
block = data[0]
# Retrieve the atom_site category table, which delineates constituent atoms1
atom_site = block.getObj("atom_site")
# Make a reference copy of the atom_site category table
atom_site_ref = copy.copy(atom_site)
# Retrieve the pdbx_struct_assembly_gen category table, which details the generation of each macromolecular assembly2
assembly_gen = block.getObj("pdbx_struct_assembly_gen")
# Retrieve the pdbx_struct_oper_list category table, which details translation and rotation
# operations required to generate/transform assembly coordinates3
oper_list = block.getObj("pdbx_struct_oper_list")
attributes = atom_site_ref.getAttributeList()
# Create a CIF file for every assembly specified in pdbx_struct_assembly_gen
for index in range(assembly_gen.getRowCount()) :
# Create a new atom_site category table for this assembly
atom_site = DataCategory("atom_site", attributes)
# Lists to hold the individual operations
oper = []
oper2 = []
# Keep track of the current atom and model number
atomNum = 1
modelNum = 0
# Retrieve the assembly_id attribute value for this assembly
assemblyId = assembly_gen.getValue("assembly_id", index)
# Retrieve the operation expression for this assembly from the oper_expression attribute
oper_expression = assembly_gen.getValue("oper_expression", index)
# Count the number of left parentheses in the operation expression
parenCount = oper_expression.count("(")
# Handles one operation assemblies (e.g., "1")
if parenCount == 0 : oper.append(oper_expression)
# Handles multiple operation assemblies, no Cartesian products (e.g., "(1-5)")
if parenCount == 1 : oper.extend(parseOperationExpression(oper_expression))
# Handles Cartesian product expressions (e.g., "(X0)(1-60)")
if parenCount == 2 :
# Break the expression into two parenthesized expressions and parse them
temp = oper_expression.find(")")
oper.extend(parseOperationExpression(oper_expression[0:temp+1]))
oper2.extend(parseOperationExpression(oper_expression[temp+1:]))
# Retrieve the asym_id_list, which indicates which atoms to apply the operations to
asym_id_list = assembly_gen.getValue("asym_id_list", index)
temp = (1 > len(oper2)) and 1 or len(oper2)
# For every operation in the first parenthesized list
for op1 in oper :
# Find the index of the current operation in the oper_list category table
op1index = 0
for row in range(oper_list.getRowCount()) :
if oper_list.getValue("id", row) == op1 :
op1index = row
break
# For every operation in the second parenthesized list (if there is one)
for i in range(temp) :
# Find the index of the second operation in the oper_list category table
op2index = -1
if (oper2) :
for row in range(oper_list.getRowCount()) :
if oper_list.getValue("id", row) == oper2[i] :
op2index = row
break
# Prepare the operation matrix
operation = prepareOperation(oper_list, op1index, op2index)
# Iterate over every atom in the atom_site reference table
for r in range(atom_site_ref.getRowCount()) :
# If the asym_id of the current atom is not in the asym_id list, skip to the next atom
if (asym_id_list.find(atom_site_ref.getValue("label_asym_id", r)) == -1) :
continue
# Retrieve the atom's row from the atom_site reference table
atom = atom_site_ref.getFullRow(r)
# Add this row to the atom_site table for this assembly
for s in range(len(attributes)) :
atom_site.setValue(atom[s], attributes[s], atomNum - 1)
# Update the atom number and model number for this row
atom_site.setValue(str(atomNum), "id", atomNum - 1)
atom_site.setValue(str(modelNum), "pdbx_PDB_model_num", atomNum - 1)
# Determine and set the new coordinates
coords = [float(atom[10]), float(atom[11]), float(atom[12]), 1.0]
sum = 0.0
xyz = ['x', 'y', 'z']
for a in range(3) :
sum = 0.0
for b in range(4) :
sum += (operation[a][b] * coords[b])
atom_site.setValue("%.3f" % sum, "Cartn_" + xyz[a], atomNum - 1)
atomNum += 1
modelNum += 1
# Write the CIF out file
block.replace(atom_site)
out = open(root + "-" + assemblyId + ".cif", "w")
pWt = PdbxWriter(out)
pWt.writeContainer(block)
out.close()